IN-MOLD CUTTING SERVO THERMOFORMING MACHINE
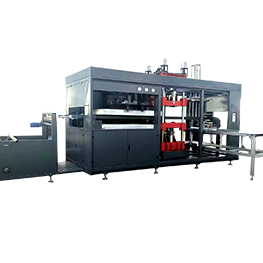
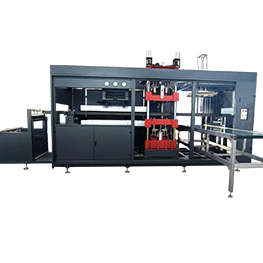
In-mold cutting servo thermoforming machine,also calledIn-mold cutting servo blister machine, integrates punching position into forming position, which greatly improves the precision of products and simplifies the structure of the machine.
In-die cutting servo thermoforming machine is developed and evolved on the basis of automatic pressure and vacuum thermoforming machine, which has higher precision and more compact structure than automatic pressure and vacuum thermoforming machine.
In-die cutting servo thermoforming machine, usually including heating station, forming punching station and stacking station and other auxiliary facilities.
The forming mechanism of the in-die cutting servo thermoforming machine is the same as that of the automatic pressure and vacuum thermoforming machine, and the products are formed through the joint action of positive pressure and vacuum. The maximum pressure of vacuum forming is one atmosphere, and the pressure of positive and negative pressure forming is positive pressure plus one atmosphere, which usually can reach 4-5 atmospheres of pressure. Under the combined action of vacuum and positive pressure of compressed air, the appearance quality and production efficiency of products have been improved obviously. But on the other hand, due to the use of positive pressure, it makes the machine clamping force multiply increase when positive and negative pressure forming at the same time use.The forming station becomes complex and bulky. So pressure and vacuum thermoforming machine relative vacuum forming machine requires higher precision and greater driving force, at the same time automatic control becomes more complex. Now CNC and PLC technology has been very mature, pressure and vacuum thermoforming to replace negative pressure forming is an inevitable trend.
The characteristics of the in-mold cutting servo forming machine is high speed, high quality, automatic. According to the different needs of the product process, the machine can be divided into two stations, three stations, four stations and even five stations.